Most Recent Arxiv Papers In Nonlinear Sciences 2|2019-07-03
Pattern Formation And Solitons
Introducing the stability catalyzer for relativistic soliton solutions (1902.02648v3)
Mohammad. Mohammadi, Ali. Reza. Olamaei
2019-02-05
For a real nonlinear Klein-Gordon (RNKG) lagrangian density with an unstable solitary wave solution (SSWS), it is shown how adding a proper additional massless term, without changing the dominant dynamical equation and other properties of the SSWS, guarantees the stability of the SSWS appreciably, i.e. it is a stability catalyzer.
Stability of bubble-like fluxons in disk-shaped Josephson junctions in the presence of a coaxial dipole current (1812.07980v3)
Alicia G. Castro-Montes, Mónica A. García-Ñustes, Jorge A. González, Juan F. Marín, Diego Teca-Wellmann
2018-12-19
We investigate analytically and numerically the stability of bubble-like fluxons in disk-shaped heterogeneous Josephson junctions. Using ring solitons as a model of bubble fluxons in the two-dimensional sine-Gordon equation, we show that the insertion of coaxial dipole currents prevents their collapse. We characterize the onset of instability by introducing a single parameter that couples the radius of the bubble fluxon with the properties of the injected current. For different combination of parameters, we report the formation of stable oscillating bubbles, the emergence of internal modes, and bubble breakup due to internal mode instability. We show that the critical germ depends on the ratio between its radius and the steepness of the wall separating the different phases in the system. If the steepness of the wall is increased (decreased), the critical radius decreases (increases). Our theoretical findings are in good agreement with numerical simulations. We discuss applications in quantum information technologies.
Coexisting Ordered States, Local Equilibrium-like Domains, and Broken Ergodicity in a Non-turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard Convection at Steady-state (1812.06002v3)
Atanu Chatterjee, Yash Yadati, Nicholas Mears, Germano Iannacchione
2018-12-14
A challenge in fundamental physics and especially in thermodynamics is to understand emergent order in far-from-equilibrium systems. While at equilibrium, temperature plays the role of a key thermodynamic variable whose uniformity in space and time defines the equilibrium state the system is in, this is not the case in a far-from-equilibrium driven system. When energy flows through a finite system at steady-state, temperature takes on a time-independent but spatially varying character. In this study, the convection patterns of a Rayleigh-B{'e}nard fluid cell at steady-state is used as a prototype system where the temperature profile and fluctuations are measured spatio-temporally. The thermal data is obtained by performing high-resolution real-time infrared calorimetry on the convection system as it is first driven out-of-equilibrium when the power is applied, achieves steady-state, and then as it gradually relaxes back to room temperature equilibrium when the power is removed. Our study provides new experimental data on the non-trivial nature of thermal fluctuations when stable complex convective structures emerge. The thermal analysis of these convective cells at steady-state further yield local equilibrium-like statistics. In conclusion, these results correlate the spatial ordering of the convective cells with the evolution of the system's temperature manifold.
An Energy Stable BDF2 Fourier Pseudo-Spectral Numerical Scheme for the Square Phase Field Crystal Equation (1906.12255v1)
Kelong Cheng, Cheng Wang, Steven M. Wise
2019-06-28
In this paper we propose and analyze an energy stable numerical scheme for the square phase field crystal (SPFC) equation, a gradient flow modeling crystal dynamics at the atomic scale in space but on diffusive scales in time. In particular, a modification of the free energy potential to the standard phase field crystal model leads to a composition of the 4-Laplacian and the regular Laplacian operators. To overcome the difficulties associated with this highly nonlinear operator, we design numerical algorithms based on the structures of the individual energy terms. A Fourier pseudo-spectral approximation is taken in space, in such a way that the energy structure is respected, and summation-by-parts formulae enable us to study the discrete energy stability for such a high-order spatial discretization. In the temporal approximation, a second order BDF stencil is applied, combined with an appropriate extrapolation for the concave diffusion term(s). A second order artificial Douglas-Dupont-type regularization term is added to ensure energy stability, and a careful analysis leads to the artificial linear diffusion coming at an order lower that that of surface diffusion term. Such a choice leads to reduced numerical dissipation. At a theoretical level, the unique solvability, energy stability are established, and an optimal rate convergence analysis is derived in the
norm. In the numerical implementation, the preconditioned steepest descent (PSD) iteration is applied to solve for the composition of the highly nonlinear 4-Laplacian term and the standard Laplacian term, and a geometric convergence is assured for such an iteration. Finally, a few numerical experiments are presented, which confirm the robustness and accuracy of the proposed scheme.
Kinetics of coarsening have dramatic effects on the microstructure: self-similarity breakdown induced by viscosity contrast (1906.12114v1)
Hervé Henry, György Tegze
2019-06-28
The viscous coarsening of a phase separated mixture is studied and the effects of the viscosity contrast between the phases are investigated. From an analysis of the microstructure, it appears that for moderate departure from the perfectly symmetric regime the self-similar bicontinuous regime is robust. However, the connectivity of one phase decreases when its volume fraction decreases or when it is becoming less viscous than the complementary phase. Eventually self-similarity breakdown is observed and characterized.
Exactly Solvable And Integrable Systems
The Elliptic Function in Statistical Integrable Models (1603.01079v2)
Kazuyasu Shigemoto
2016-03-03
We examine the group theoretical reason why various two dimensional statistical integrable models, such as the Ising model, the chiral Potts model and the Belavin model, becomes integrable. The symmetry of these integrable models is SU(2) and the Boltzmann weight can be parametrized by the elliptic function in many cases. In this paper, we examine the connection between the SU(2) symmetry and the elliptic function in the statistical integrable models.
The Unified Soliton System as the 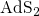 System (1906.10796v2)
System (1906.10796v2)
Masahito Hayashi, Kazuyasu Shigemoto, Takuya Tsukioka
2019-06-26
We study the Riemann geometric approach to be aimed at unifying soliton systems. The general two-dimensional Einstein equation with constant scalar curvature becomes an integrable differential equation. We show that such Einstein equation includes KdV/mKdV/sine-Gordon equations.
Dissipative Quantum Ising chain as a non-Hermitian Ashkin-Teller model (1904.12505v2)
Naoyuki Shibata, Hosho Katsura
2019-04-29
We study a quantum Ising chain with tailored bulk dissipation, which can be mapped onto a non-Hermitian Ashkin-Teller model. By exploiting the Kohmoto-den Nijs--Kadanoff transformation, we further map it to a staggered XXZ spin chain with pure-imaginary anisotropy parameters. This allows us to study the eigenstates of the original Liouvillian in great detail. We show that the steady state in each parity sector is a completely mixed state. The uniqueness of each is proved rigorously. We then study the decay modes on the self-dual line corresponding to the uniform XXZ chain and obtain an exact formula for the Liouvillian gap
, the inverse relaxation time, in the thermodynamic limit. The gap
as a function of dissipation strength
has a cusp, implying a kind of phase transition for the first decay mode.
Revisiting generalized Hulthén potentials (1906.11625v1)
C. Quesne
2019-06-27
A relation between the deformed Hulth'en potential and the Eckart one is used to write the bound-state wavefunctions of the former in terms of Jacobi polynomials and to calculate their normalization coefficients. The shape invariance property of the Eckart potential in standard first-order supersymmetric quantum mechanics allows to easily rederive the set of extended deformed Hulth'en potentials, recently obtained by using the Darboux-Crum transformation, and to show that their spectra and normalized wavefunctions follow without any further calculation. Furthermore, by taking advantage of other known rational extensions of the Eckart potential obtained in first-order supersymmetric quantum mechanics, novel extensions of the deformed Hulth'en potential are constructed, together with their bound-state spectra and wavefunctions. These new extensions belong to three different types, the first two being isospectral to some previously obtained extensions and the third one with an extra bound state below their spectrum.
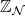 graded discrete integrable systems and Darboux transformations (1906.11593v1)
graded discrete integrable systems and Darboux transformations (1906.11593v1)
Ying Shi
2019-06-27
We present the Darboux transformations for a novel class of two-dimensional discrete integrable systems named as
graded discrete integrable systems, which were firstly proposed by Fordy and Xenitidis within the framework of
graded discrete Lax pairs very recently. In this paper, the
graded discrete equations in coprime case and their corresponding Lax pairs are derived from the discrete Gel'fand-Dikii hierarchy by applying a transformation of the independent variables. The construction of the Darboux tranformations is realised by considering the associated linear problems in the bilinear formalism for the
graded lattice equations. We show that all these
graded equations share a unified solution structure in our scheme.

Don't forget to Follow and Resteem. @complexcity
Keeping everyone inform.