3.1 How Much Does the Economy Produce?
The Production Function
Factors of production
Capital
Labor
Others (raw materials, land, energy)
Productivity of factors depends on technology and management
The production function
Y = AF(K,N)
Parameter A is “total factor productivity”
Application: The production function of the U.S. economy and U.S. productivity growth
Cobb-Douglas production function works well for U.S. economy:
Y = A K0.3 N0.7
Data for U.S. economy—Table 3.1
Productivity growth calculated using production function
Productivity moves sharply from year to year
Productivity grew slowly in the 1980s and the first half of the 1990s
Table 3.1 US Production Function, 1980–2001
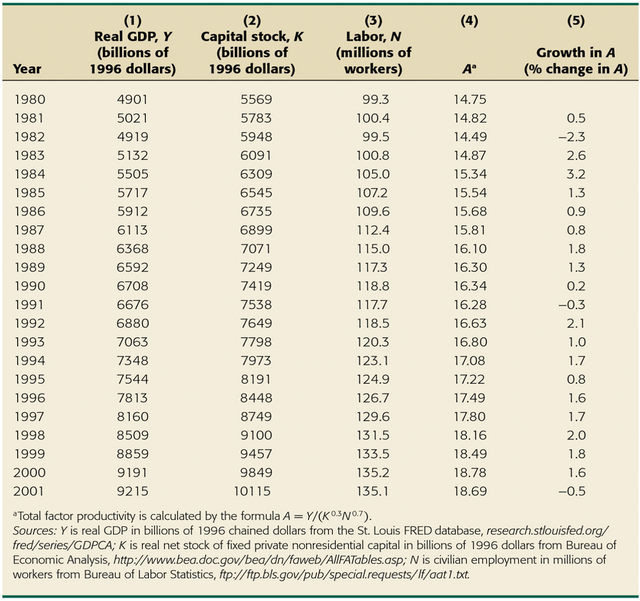
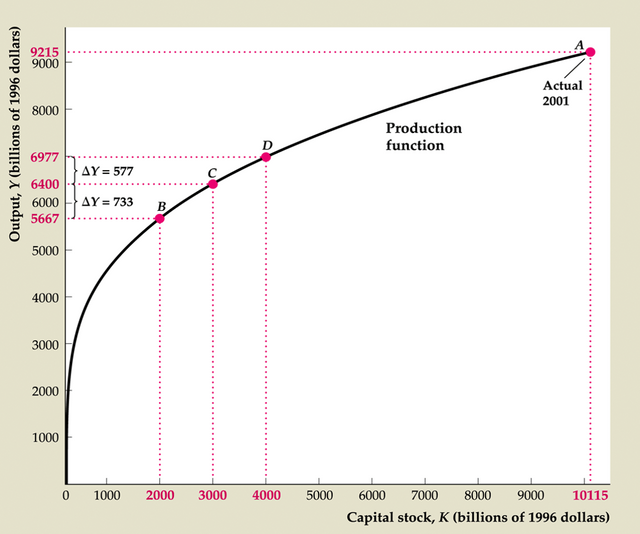
Figure 3.1 The production function relating output and capital
The shape of the production function
Two main properties of production functions
Slopes upward: more of any input produces more output
Slope becomes flatter as input rises: diminishing marginal product as input increases
Graph production function (Y vs. one input; hold other input and A fixed)
Marginal product of capital, MPK = ΔY/ΔK (Key Diagram 1; Fig. 3.2)
Equal to slope of production function graph (Y vs. K)
MPK always positive
Diminishing marginal productivity of capital
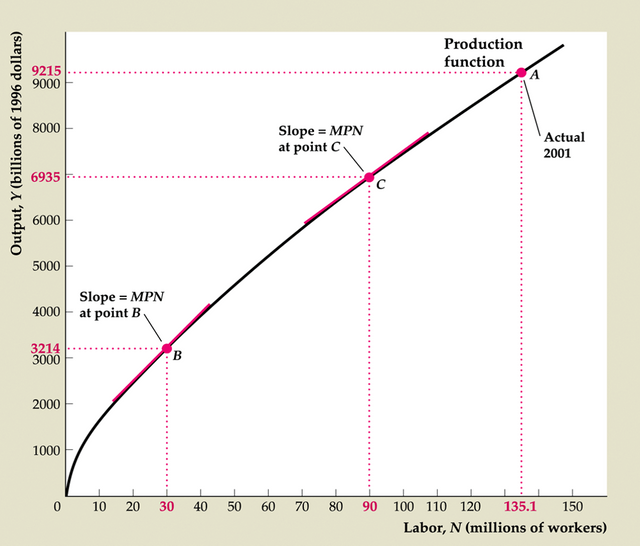
Marginal product of labor, MPN = ΔY/ΔN (Fig. 3.3)
Equal to slope of production function graph (Y vs. N)
MPN always positive
Diminishing marginal productivity of labor
Key Diagram 1 The production function
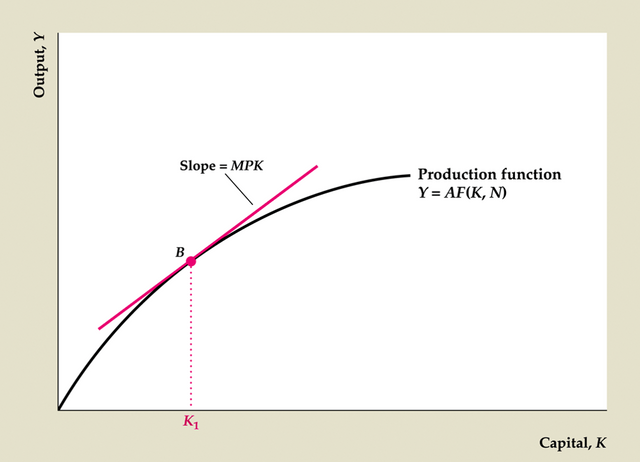
Figure 3.2 The marginal product of capital
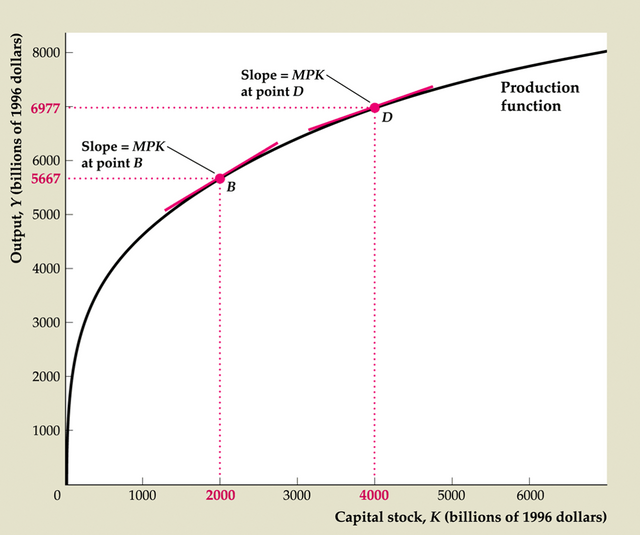
Figure 3.3 The production function relating output and labor