Tissue regeneration in rodents and reptiles
Tissue regeneration in rodents and reptiles


And if the human body could heal itself like a lizard that regenerates its tail, Chinese scientists are getting closer to achieving it and in a surprising experiment, they reactivated in mice an ancestral genetic code that seemed to have been lost during evolution and with that they managed to make the mice regenerate complex tissues that they normally could not.
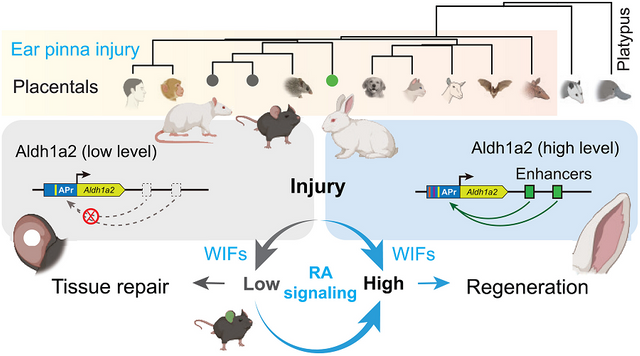

This technique of borrowing genetic elements from species with high regenerative power represents a new approach in genetic engineering. The manipulation proved to be safe in the context studied, with functional regeneration and without uncontrolled tissue growth.
