Hypothesis Testing with Chi-Square Method!!!
What is hypothesis
A hypothesis is a guess or idea about something that can be tested.
Example 01:-
A nurse believes a new training method improves communication with patients.
Example 02:-
A doctor thinks a medicine work for 90% cases it's given to.
Types of hypothesis
1:Alternative hypothesis:-
Alternative hypothesis is opposite to the null hypothesis.It says that there is a difference or effect.
Example:
The new medicine works better than the old one.
2:Null hypothesis:-
The Null hypothesis is a statement that says there is no effect or no difference.It assumes that nothing has changed.
Example:
The new medicine doesn't works better than old one.
(Chi-Square Test)
The Chi-Square is a non parametric statistical test used to determine whether there is a significant association between categorical variables.
Example:-
The Chi-Square Test can be use to check of material status differs by education level e.g,matric,intermediate and graduate individual being single or married.
(Types of Chi-Square Test)
1: Chi-Square goodness of fit test.
2: Chi-Square Test of independence.
(Formula)
X^2=E(O-E)^2/E
01-Chi-Square goodness of fit test)
It is used to determine whether the observed distribution of a categorical variables matches an expected distribution.
(Uses)
It is used to test if the data follows a theoretical data.
(E.g uniform, binomial.)
Common in quality control, genetics,dice/fairness,etc.
(distinguishing characteristic)
-Only one categorical variable.
-Null hypothesis(Ho): observed=Expected.
-Alternative hypothesis(HA): observed≠Expected.
(Steps for test)
1-Degree of freedom.
DF=N-1
2-Expected Frequency.
Expected Frequency=np
02(Chi-Square Test of independence)
It tests whether two categorical variables are independent or associated with one another.
(Uses)
To analyze relationships between two variables in one sample.
Common in survey analysis, medical research, education and studies etc.
(Distinguishing characteristic)
-Null hypothesis(Ho): variables are independent.
-Alternative hypothesis(HA): variables are associated.
(Steps for test)
1-Degree of freedom:-
DF=(r-1)(c-1)
2-Expected Frequency:-
E=RT×CT/N
(Assumption for Chi-Square Test)
1-All the observation must be "independent". No individual should be included twice or a number of times in a sample.
2-The total number of observation should be large. The Chi-Square Test should not be if n<50.
3-All the events must be mutually exclusive.
4-For comparison purpose,the data must be in "original units".
5-Observation must be categorical not continuous.
6-A sample size can lead to mislead conclusion.
7-Data must be collected randomly to avoid "bias".
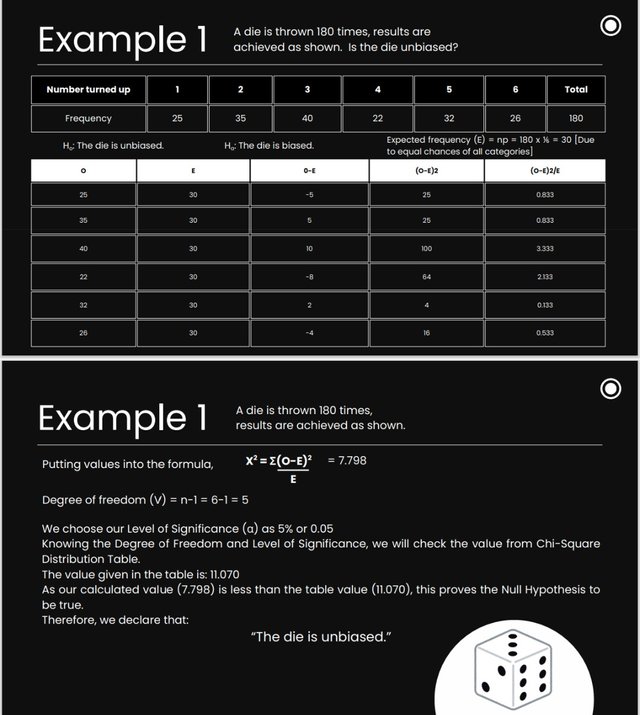
(More solved Examples)
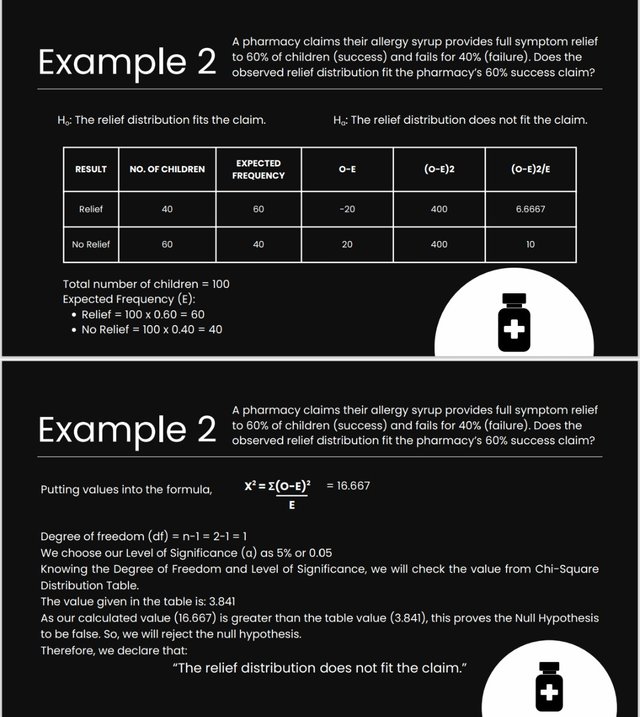
(Example 01)
(Common mistakes in Chi-Square Tests)
1-Using it with small sample size.
2-Ignoring assumptions of independence.
3-Incorrect degree of freedom.
4-Using percentages instead of frequencies.
(Limitations of Chi-Square Test)
1-Sensitive to the sample size.
2-Only test for association,not strength or directions.
3-Limited to the frequency data.
4-Cannot be used with expected frequencies of zero.
(Applications of Chi-Square Test)
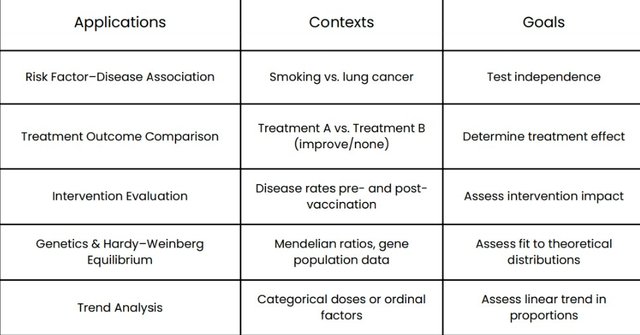
(Practical life applications)
1-Medical research
checking if a new drug's success rate differs across age groups.
2-Market research
Studying if product preference depends upon genders.
3-Manufacturing/quality control
Checking if defects occurs production batches
4-Elections/politics
Determining if voting preference is linked to region
5-Sociology
Studying if crime rate is related to time of day.
6-Genetics
Comparing observed and expected frequencies of traits in offsprings.
(REFERENCES)
Chi-Square test on JMP Statistical Discovery.
Fundamental of biostatistics(7th Ed.)by Bernard Rosner...
Kind Regards:-
@steemsial