05-08-2025 - Exercise - Linear Programming (LP) [EN]-[IT]
Cover background image generated with AI, software used: copilot microsoft
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
[ENGLISH]
05-08-2025 - Exercise - Linear Programming (LP) [EN]-[IT]
Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
With this post, I would like to provide some brief insights into the topic mentioned above by completing some exercises.
The context in which we operate is that of Operations Research
(code notes: MOD-90)
Linear Programming (LP)
Linear programming is a mathematical technique designed to find the best solution to a complex problem.
Below, I would like to demonstrate how linear programming could be used in a simple case.
First, let's remember that linear programming has three basic concepts.
1-The Objective Function
2-The Constraints
3-The Decision Variables
The Problem
Let's imagine a company produces two products; we'll call these two products A and B.
Each unit of A requires 2 hours of labor, while each unit of B requires 1 hour of labor. The company has a maximum of 100 hours of labor available.
The profit for each unit of A is €40, while for B it is €30.
Our goal will be to maximize profit.
Identification of Decision Variables
X = number of units of product A to be produced
Y = number of units of product B to be produced
Let's now identify the three basic concepts by collecting the data provided previously.
Objective Function
Constraints
The constraint is the available time.
Note: X and Y cannot be negative.
Analysis
Let's represent the constraint graphically, recalling that
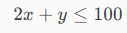
So
with x=0, y=100
with y=0, x=50
So the line is as follows:
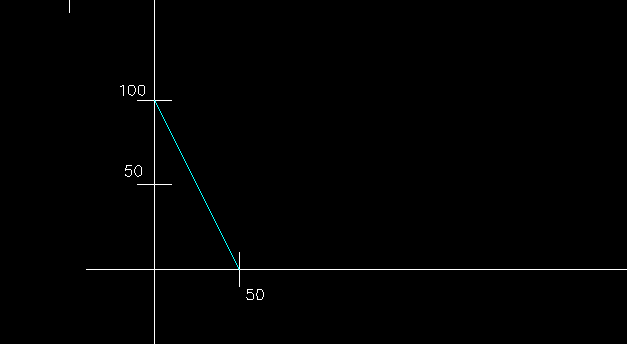
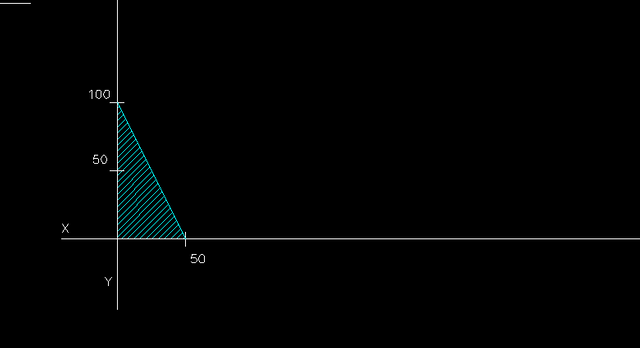
Adding the non-negativity constraints, we have that the feasible area is the triangle shown in the figure here. Below:
The Solution
Starting from our objective function
To find the maximum, let's check the vertices of the blue triangle shown in the figure.
always based on
Z=40x+30y
We will therefore have that
At the point (0,0): Z=0
At the point (0,100): Z=40 * 0 + 30 * 100 = 3000
At the point (50,0): Z=40 * 50 + 30 * 0 = 2000
Result
The maximum is obtained at (0,100), which means that the best solution is to produce only B. The maximum profit will be 3000
Conclusions
This is a classic example of a linear programming problem because we have only two variables x and y, a main constraint: time, and a very clear objective function: profit maximization.
Question
Have you ever heard of linear programming? Did you study it in school or do these calculations in your job?

[ITALIAN]
05-08-2025 - Esercizio - Programmazione lineare PL [EN]-[IT]
Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Con questo post vorrei fornire alcune brevi nozioni a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto svolgendo degli esercizi.
Il contesto in cui operiamo è quello della Ricerca Operativa
(code notes: MOD-90)
Programmazione lineare PL
La programmazione lineare è una tecnica matematica che è stata ideata per trovare la miglior soluzione ad un problema complesso.
Qui di seguito vorrei mostrare come potrebbe venir usata la programmazione lineare in un caso semplice.
Innanzitutto ricordiamo che nella programmazione lineare abbiamo 3 concetti base.
1-La funzione obiettivo
2-I vincoli
3-Le variabili decisionali
Il problema
Immaginiamo che un'azienda produca due prodotti, questi due prodotti li chiamiamo A e B.
Ogni unità di A richiede 2 ore di lavoro mentre ogni unità di B richiede 1 ora di lavoro. L'azienda ha a disposizione al massimo 100 ore di lavoro.
Il profitto di ogni unità A è 40€, mentre per B è 30€.
Il nostro obiettivo sarà quello di massimizzare il profitto.
Identificazione delle variabili decisionali
X = numero di unità del prodotto A da produrre
Y = numero di unità del prodotto B da produrre
Andiamo ora ad identificare i tre concetti base raccogliendo i dati forniti in precedenza.
Funzione obiettivo
I vincoli
Il vincolo è il tempo disponibile
Nota: X ed Y non possono essere negativi.
Analisi
Rappresentiamo il vincolo graficamente ricordando che
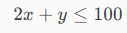
Quindi
con x=0, y=100
con y=0, x=50
Quindi la retta è la seguente
Aggiungendo i vincoli di non negatività avremo che l'area ammissibile è il triangolo rappresentato in figura qui sotto:
La soluzione
Partendo dalla nostra funzione obiettivo
Per ricavare il massimo andiamo a fare la verifica dei vertici del triangolo azzurro mostrato in figura.
sempre in base a
Z=40x+30y
Avremo quindi che
Nel punto (0,0): Z=0
Nel punto (0,100): Z=40 * 0 + 30100=3000
Nel punto (50,0): Z=40 50 +30 * 0 =2000
Risultato
Il massimo si ottiene in (0,100), il che significa che la soluzione migliore è produrre solo B. Il profitto massimo sarà 3000
Conclusioni
Questo è un esempio classico di un problema di programmazione lineare in quanto abbiamo solo due variabili x e y, un vincolo principale che è il tempo e una funzione obiettivo ben chiara che è la massimizzazione del profitto.
Domanda
Avete mai sentito parlare di programmazione lineare? L'avete studiata a scuola oppure avete fatto questi calcoli nel lavoro che svolgete?
THE END


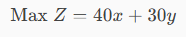
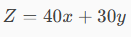
I saw this topic in one of the subjects of the syllabus at the university, but I don't remember well which one.
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
This post has been upvoted by @italygame witness curation trail
If you like our work and want to support us, please consider to approve our witness
Come and visit Italy Community