NASA APOD #682-691
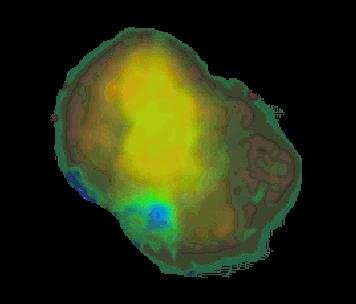
#682 A Galactic Cloud of Antimatter
Credit: May 01, 1997
“The center of our Milky Way Galaxy is full of surprises. Its latest spectacular is a mysterious cloud glowing in gamma rays produced by annihilating antimatter particles! Star Trek fans are all too familiar with the consequences of mixing matter (electrons) and antimatter (positrons) - the particles catastrophically annihilate converting their masses to energy according to Einstein's famous E=mc2. Positron/electron annihilation energy is emitted as gamma rays with photon energies of 511,000 electron volts. Searching for these high energy photons, the OSSE instrument onboard NASA's orbiting Compton Gamma Ray Observatory has recently produced this map of the Galactic Center (GC) region. As anticipated, it shows annihilation gamma rays as a bright spot at the GC with fainter horizontal emission from the galactic plane. Astoundingly, it also reveals a large and unexpected cloud of annihilation radiation, probably about 4,000 light years across, extending nearly 3,500 light years above the GC. What could have created this cloud? Associated with no previously known object, it seems to imply that a fountain of antimatter positrons streams from the GC. Present guesses about the source of the positrons include the violent and exotic environments surrounding starbirth, neutron star collisions, and black holes at the GC. Are there other such clouds in our Galaxy?"
Copyright: Public domain
#683 X-Rays From IC 443
Credit: May 02, 1997
“The life-cycles of stars help drive the ecology of our Galaxy, churning, processing, and redistributing matter. Massive stars reach a spectacular evolutionary endpoint - supernovae explosions which blast off their outer layers, violently merging stellar material with the gas and dust of the Milky Way. The supernova remnant IC 443 is typical of the aftermath. Seen in this false color X-ray image are the shocked, expanding shells of gas from a star which exploded thousands of years ago. Known to be interacting with galactic molecular clouds, the expanding supernova remnant was also recently discovered to have regions of intense higher energy X-ray emission (coded blue in this map) near the molecular cloud boundaries. This X-ray emission may indicate that electrons are being accelerated within the remnant, gaining in energy as they surf back and forth across the expanding shock wave. If so, IC 443 could also be one source of our Galaxy's puzzling high energy cosmic-rays."
Copyright: Public domain
#684 Giant Cluster Bends, Breaks Galaxy Images
Credit: May 03, 1997
“What are those strange blue objects? Many are images of a single, unusual, beaded, blue, ring-like galaxy which just happens to line-up behind a giant cluster of galaxies. Cluster galaxies here appear yellow and -- together with the cluster's dark matter -- act as a gravitational lens. A gravitational lens can create several images of background galaxies, analogous to the many points of light one would see while looking through a wine glass at a distant street light. The distinctive shape of this background galaxy -- which is probably just forming -- has allowed astronomers to deduce that it has separate images at 4, 8, 9 and 10 o'clock, from the center of the cluster. Possibly even the blue smudge just left of center is yet another image! This spectacular photo from HST was taken in October 1994. The first cluster lens was found unexpectedly by Roger Lynds (NOAO) and Vahe Petrosian (Stanford) in 1986 while testing a new type of imaging device. Lensed arcs around this cluster, CL0024+1654, were first discovered from the ground by David Koo (UCO Lick) in 1988."
Copyright: Public domain
#685 The Last Moon Shot
Credit: May 04, 1997
“In 1865 Jules Verne predicted the invention of a space capsule that could carry people. In his science fiction story "From the Earth to the Moon", he outlined his vision of a cannon in Florida so powerful that it could shoot a "Projectile-Vehicle" carrying three adventurers to the Moon. Over 100 years later, NASA, guided by Wernher Von Braun's vision, produced the Saturn V rocket. From a spaceport in Florida, this rocket turned Verne's fiction into fact, launching 9 Apollo Lunar missions and allowing 12 astronauts to walk on the Moon. Pictured is the last moon shot, Apollo 17, awaiting a night launch in December of 1972. Spotlights play on the rocket and launch pad while the full Moon looms in the background. Humans have not walked on the lunar surface since. Should we return to the Moon?"
Copyright: Public domain
#686 Sunset with Hale-Bopp at Keck
Credit: May 05, 1997
“A famous star cluster and observatory highlight this picture of Comet Hale-Bopp. Taken last week from the observatory summit of Hawaii's Mauna Kea Volcano, the dome of the new 10-meter Keck II telescope appears silhouetted on the lower left. Comet Hale-Bopp is visible on the upper right, and the Pleiades star cluster is visible below the comet. Normally sunset and clouds are to be avoided when making astronomical observations, but Comet Hale-Bopp is not a normal astronomical object. In fact, were it cloudless, Professor Keel would be inside NASA's nearby IRTF dome preparing to observe something else. Comet Hale-Bopp continues to look impressive, although it is fading and moving towards the south."
Copyright: Public domain
#687 NGC4039: Starbirth and Galaxy Death
Credit: May 06, 1997
“Do star clusters form when galaxies collide? Quite possibly, according to Hubble Space Telescope observations of the "Antennae", two galaxies thought to be in the early stages of a collision. As NGC 4038 and NGC 4039 slowly merge, the combined gravity of each pulls the other apart, huge gas clouds collide, and new bright stars and dark dust are dispersed. Many blue knots of stars appear to be newly formed globular clusters. Red star knots are particularly interesting, as they might be globular clusters that have not yet expelled early dust from their system. The above picture is centered around the smaller of the two interacting galaxies: NGC 4039. The color contrast in the above three-color mosaic was chosen to highlight extended features."
Copyright: AURA
#688 Ultraviolet Venus
Credit: May 07, 1997
“The forecast for Venus is cloudy, cloudy, cloudy. Although similar to the Earth in size and mass, Venus' slightly closer orbit to the Sun create for it a much thicker atmosphere and a much hotter surface. The thick atmosphere was photographed above in ultraviolet light in 1979 by the Pioneer Venus Orbiter. Whether or not Venus has a moon was the center of a great controversy in the 1700s and 1800s. Today we know Venus has no natural satellites. Venus's extremely uncomfortable climate was likely caused by a runaway greenhouse effect. Could Earth ever undergo runaway greenhouse heating like Venus?"
Copyright: Public domain
#689 Detailing Hale-Bopp
Credit and Copyright: May 08, 1997
“This enhanced composite image detailing structure in the coma and dust tail of Hale-Bopp was recorded May 5 - one day before the comet's passage from north to south across the plane of Earth's orbit. As the comet descends into murky twilight for northern hemisphere observers it will become increasingly easy to view from the south. Along with Southern Hemisphere observers, astronomers and a fleet of spacecraft of the International Solar-Terrestrial Physics program have been anxiously awaiting this north/south crossing. The comet's interaction with the changing equatorial solar wind and magnetic field during this crossing is expected to produce distortions and disconnections of Hale-Bopp's ion tail. Whisker-like structures, probably part of the ion tail, are visible above extending from the lower left of the bright coma."
Copyright: Public domain
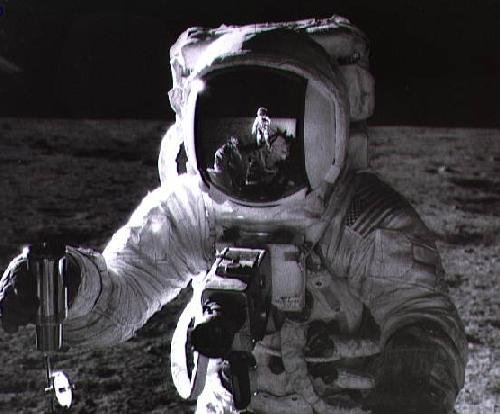
#690 Apollo 12: Self-Portrait
Credit: May 09, 1997
“Is it art? In November of 1969, Apollo 12 astronaut-photographer Charles "Pete" Conrad recorded this masterpiece while documenting colleague Alan Bean's lunar soil collection activities on the Oceanus Procellarum. The image is dramatic and stark. Bean is faceless - the harsh environment of the Moon's Ocean of Storms is echoed in his helmet's perfectly composed reflection of Conrad and the lunar horizon. Works of photojournalists orginally intent on recording the human condition on planet Earth, such as Lewis W. Hine and Margaret Bourke-White are widely regarded as photographic art. Similarly many documentary astronomy and space images can be appreciated for their artistic and esthetic appeal."
Copyright: Public domain
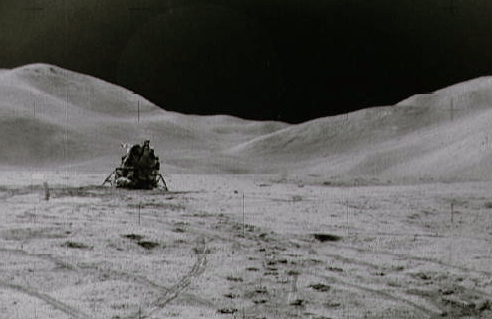
#691 Apollo 15's Home on the Moon May 10, 1997
“Could you ever call this place home? The lunar module shown above, named "Falcon," served as home for Apollo 15 astronauts David Scott and James Irwin during their stay on the Moon in July and August 1971. Meanwhile, astronaut Alfred Worden circled in the command module overhead. Harsh sunlight on the grey lunar surface lends the image an eerie quality, while the Lunar Apennine Mountains frame the background with Mount Hadley Delta visible on the right. Visible in the foreground are tracks from the first Lunar Roving Vehicle, an electric car which enabled the astronauts to explore extended areas on the lunar surface. Apollo 15 confirmed that most lunar surface features were created by impacts. Rocks returned by the Apollo 15 crew included green glasses whose formation mechanism is still unclear."
Copyright: Public domain
Upvote! Resteem! Comment! As you like it! Thank you for attention!








Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap970501.html